Cloud Computing Solutions
Cloud computing solutions refer to the various services, platforms, and resources delivered over the internet through a network of remote servers. Instead of relying on a local server or a personal computer to handle applications, store data, or perform computing tasks, cloud computing allows users to access computing resources on-demand from a remote location. Cloud computing solutions are characterized by their scalability, flexibility, and the ability to pay for resources on a consumption basis. Here are some key components and types of cloud computing solutions:
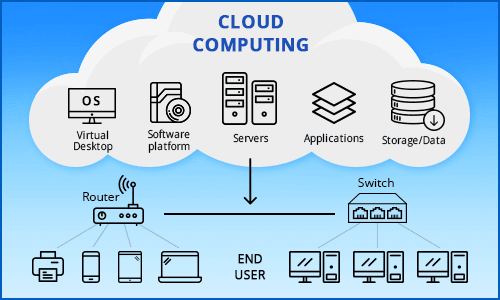
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS provides virtualized computing infrastructure over the internet. Users can rent virtual machines, storage, and networking resources on a pay-as-you-go basis. Examples of IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS offers a platform that includes a set of tools, services, and development frameworks for building, testing, and deploying applications. PaaS eliminates the need for users to manage the underlying infrastructure. Examples include Heroku, Google App Engine, and Microsoft Azure App Service.
Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. Users can access the software through a web browser without the need for installation or maintenance. Common examples of SaaS include Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, Salesforce, and Dropbox.
Serverless Computing: Serverless computing, also known as Function as a Service (FaaS), allows developers to run individual functions or pieces of code without managing the underlying infrastructure. This model is event-driven, and users are billed based on the actual execution of functions.
Cloud Storage: Cloud storage solutions provide scalable and secure storage for data. Users can store and retrieve data over the internet, and these services often include features like data redundancy, versioning, and access controls. Examples include Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, and Microsoft Azure Blob Storage.
Database as a Service (DBaaS): DBaaS offers managed database services in the cloud. It includes features such as automatic backups, scaling, and maintenance, allowing users to focus on using the database rather than managing its infrastructure. Examples include Amazon RDS, Azure SQL Database, and Google Cloud SQL.
Cloud Security Solutions: Cloud security services help protect data, applications, and infrastructure in the cloud. This includes identity and access management, encryption, threat detection, and security monitoring. Examples include AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), Azure Active Directory, and Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) tools.
Containerization and Orchestration: Cloud computing often involves the use of containerization technologies like Docker and container orchestration platforms like Kubernetes. These tools facilitate the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Services: Cloud providers offer AI and ML services, allowing organizations to leverage pre-built models and tools for tasks such as image recognition, natural language processing, and predictive analytics. Examples include AWS SageMaker, Azure Machine Learning, and Google Cloud AI Platform.
Cloud computing solutions offer businesses and individuals the ability to access a wide range of computing resources without the need for significant upfront investment in hardware and infrastructure. They provide flexibility, scalability, and the ability to quickly adapt to changing business needs.